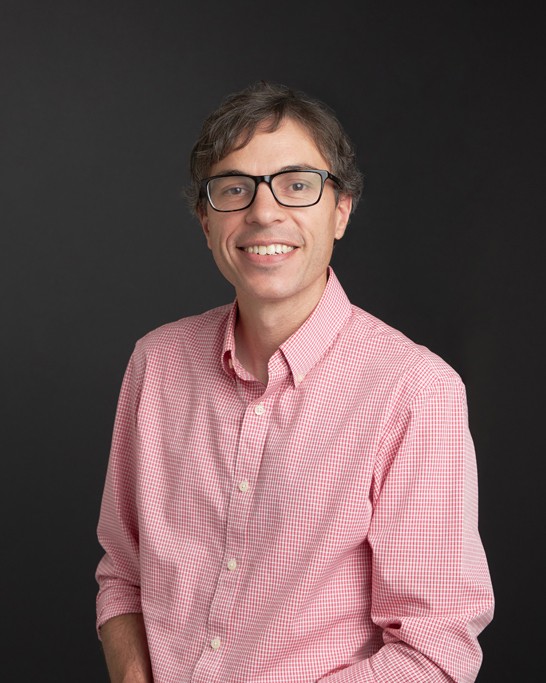

245 Beacon Street 528D
Telephone: 617-552-6905
Email: george.mohler@bc.edu
Statistical and deep learning approaches to solving problems in spatial, urban and network data science. Several current projects include modeling and causal inference for overdose and social harm event data, fairness and interpretability in criminal justice forecasting, and modeling viral processes and link formation on networks using a combination of point processes and neural networks.
R. Pandey, J. Carter, J. Hill and G. Mohler. Rewiring police officer training networks to reduce forecasted use of force. Proceedings of 29th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, (KDD 2023).
Ray, B., Mohler, G., Korzeniewski, S., Carroll, J., del Pozo, B., Victor, G., Hedden, B., & Hyun, P. Spatiotemporal analysis exploring the effect of law enforcement drug market disruptions on overdose. To appear in the American Journal of Public Health.
X. Miscouridou, S. Bhatt, G. Mohler, S. Flaxman, & S. Mishra. Cox-Hawkes: doubly stochastic spatiotemporal Poisson processes. To appear in Transactions on Machine Learning Research.
Badirli, S., Picard, C. J., Mohler, G., Richert, F., Akata, Z., & Dundar, M. (2023). Classifying the unknown: Insect identification with deep hierarchical Bayesian learning. Methods in Ecology and Evolution.
Mohler, G., & Mateu, J. (2023). Second order preserving point process permutations. Stat, e558.
Piza, E. L., Hatten, D. N., Carter, J. G., Baughman, J. H., & Mohler, G. O. (2023). Gunshot Detection Technology Time Savings and Spatial Precision: An Exploratory Analysis in Kansas City. Policing: A Journal of Policy and Practice, 17.
Chiang, W. H., & Mohler, G. (2022, December). Hawkes Process Multi-armed Bandits for Search and Rescue. In 2022 21st IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA) (pp. 278-285). IEEE.
Khorshidi, S., Wang, B., & Mohler, G. (2022, December). Adversarial Attacks on Deep Temporal Point Process. In 2022 21st IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
MacDonald, J., Mohler, G., & Brantingham, P. J. (2022). Association between race, shooting hot spots, and the surge in gun violence during the COVID-19 pandemic in Philadelphia, New York and Los Angeles. Preventive medicine, 165, 107241.
Brantingham, P. J., Mohler, G., & MacDonald, J. (2022). Changes in public–police cooperation following the murder of George Floyd. PNAS Nexus, 1(5).
Short, M. B., & Mohler, G. O. (2022). A fully Bayesian tracking algorithm for mitigating disparate prediction misclassification. International Journal of Forecasting.
Sledge, D., Thomas, H. F., Hoang, B. L., & Mohler, G. (2022). Impact of Medicaid, Race/Ethnicity, and Criminal Justice Referral on Opioid Use Disorder Treatment. The Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law, JAAPL-210137.